HCC Part 2: Hepatocarcinogenesis: Molecular & Cellular mechanism
- A process if gradual transformation of non-malignant cells into HCC
- Cell of origin: Mature Hepatocytes vs Intrahepatic stem cells
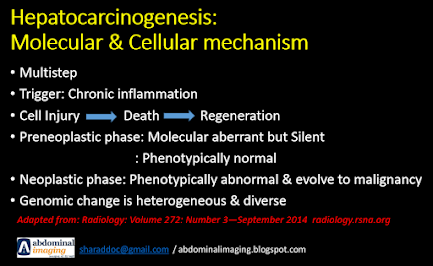
- Complex multi-step process
- Chronic inflammation plays a pivotal role due to repeated cycles of cell injury, death and regeneration.
- The new environment leads to:
- Aberrant cell signaling,
- Epigenetic changes,
- Mutational events
- Accumulation of genetic damage
- Two phase:
1. Preneoplastic phase (Morphological silent):
- Precedes years & decades before cirrhosis is established
- Runs parallel to fibrosis & cirrhosis
- Molecular aberrant but phenotypically normal
- Few or no structural changes in the genes or chromosomes
2. Neoplastic phase (structural alterations):
- Cells acquire progressive atypical phenotypic features
- Evolve to frank malignancy
Genomic changes are Heterogeneous & diverse
Several molecular variants may be produced with different growth properties in the same liver in different regions.
Phenotype:
- Hepatocellular phenotype
- Cholangiocellular phenotype
- Combined or mixed features
Prepared by : Dr. Sharad Maheshwari
11.7.2023
Updated:
Reference:
Lumeen Paramedical offers a comprehensive B.Voc in Radiology in Delhi, designed to equip students with essential skills in medical imaging. This three-year program combines theoretical knowledge with practical training, preparing graduates for rewarding careers as radiologic technologists and imaging specialists in the healthcare sector.
ReplyDelete