How to differentiate Calcium calculus from Urate calculus
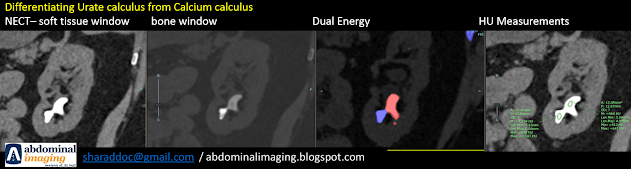
Fig. 1: Sagittal view of left kidney in soft tissue window, shows two calculi with same degree of attenuation. Fig. 2: In the same plane as above in bone window, the attenuation is different. The lower and smaller stone is more dense and homogeneous, as compared to the other bigger calculus. Fig. 3: Dual energy scan shows, the lower calculus as blue, which is assigned color for calcium and other calculus as red, color assigned for urate calculus. Fig. 4: HU measurement - the calcium calculus has HU of 1200 and the urate calculus has HU value of 560.
1. Clinical History:
Urate - Associated with high build up of uric acid. Certain conditions like
gout or life style issues like alcohol intake and excessive animal protein.
Calcium -Associated with high levels of calcium or oxalate in the body.
Some of the patients are stone formers. diet rich in protein,
oxalate, salt and fructose. Lifestyle disease like obesity. Medical
condition like hyperparathyroidism or inflammatory bowel
disease. Certain GI surgeries like bypass increase the risk.
2. Lab:
Urate - Urinary pH less than 5.5, crystals in the urine or urease positive
bacteria in urine.
Calcium -Associated with high levels of calcium or oxalate in the body.
.
3. Appearance and HU values in conventional CT scan
HU Values cannot confidently differentiate urate from calcium stones.
Urate - Urate stones are softer and less dense (usually HU is below
500 for a 4 mm stone). Usually are not seen on abdominal X-Rays
Are heterogeneous and may have less dense areas. The more
likely take the shape of the calyx and be staghorn types.
Calcium -High HU values like 800 or will be almost always be a calcium
stone. Calcium stones are more homogeneously dense
4. Dual energy scans
These are scan done at the same time using two different kVp. Change in attenuation by the stone at different kVp is a function of the chemical composition. The sensitivity and specificity of dual energy scans is > 95 % in various studies.
A color is assigned based on the chemical composition. We have assigned red color to the urate calculus and blue to calcium calculus.
Below is a case where the same calculus has both urate and calcium contents
Detailed description of the principles of dual energy are outside the purview of this blog.
Prepared by Dr. Sharad Maheshwari
11.12.2022
Updated: 15.11.2022
References:

Comments
Post a Comment